#Black fungus disease #COVID
- dinesh madduri
- May 11, 2021
- 3 min read
Updated: May 21, 2021
Zygomycosis or mucormycosis - Angio- invasive life threatnening disease
Causative agent
aseptate fungi Eg: Rhizopus, Mucor and Absidia
Where is this fungus present ?
Everywhere around us
How do they survive in human body ?
Agents of mucormycosis feed on iron in our body . So conditions with increased iron load are at higher risk of developing mucormycosis,
Who are at risk ?
Uncontrolled Diabetes ,Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is the most important risk factor
Extensive use of immunosuppressive drugs - steroids ,toclizumab
Extensive use of broad-spectrum antibiotics
immunodeficiency
Cancer
End stage renal disease
Patients taking iron therapy or deferoxamine (iron chelator)
Defects in phagocytic functions (e.g. neutropenia ).

Why COVID patients are at increased risk ?
COVID patients using mask , oxygen humidifiers and ventilators in hospital which are not properly sanitized can lead to fungus growth
In covid even though serum iron levels decrease intracellular iron levels increase so during recovery from covid these intracellular cells undergo degeneration leading to release of iron and along with acidic pH helps fungus to grow
Why the black fungus is life threatening ?
These fungi are angioinvasive i.e directly invade blood vessels . Literally they may invade any part of the body .They rapidly progress in the body even a slight
delay in the diagnosis or appropriate management can have devastating implications on patient survival .
Most common organs involved are nose , brain , eye , lungs , skin , intestines.
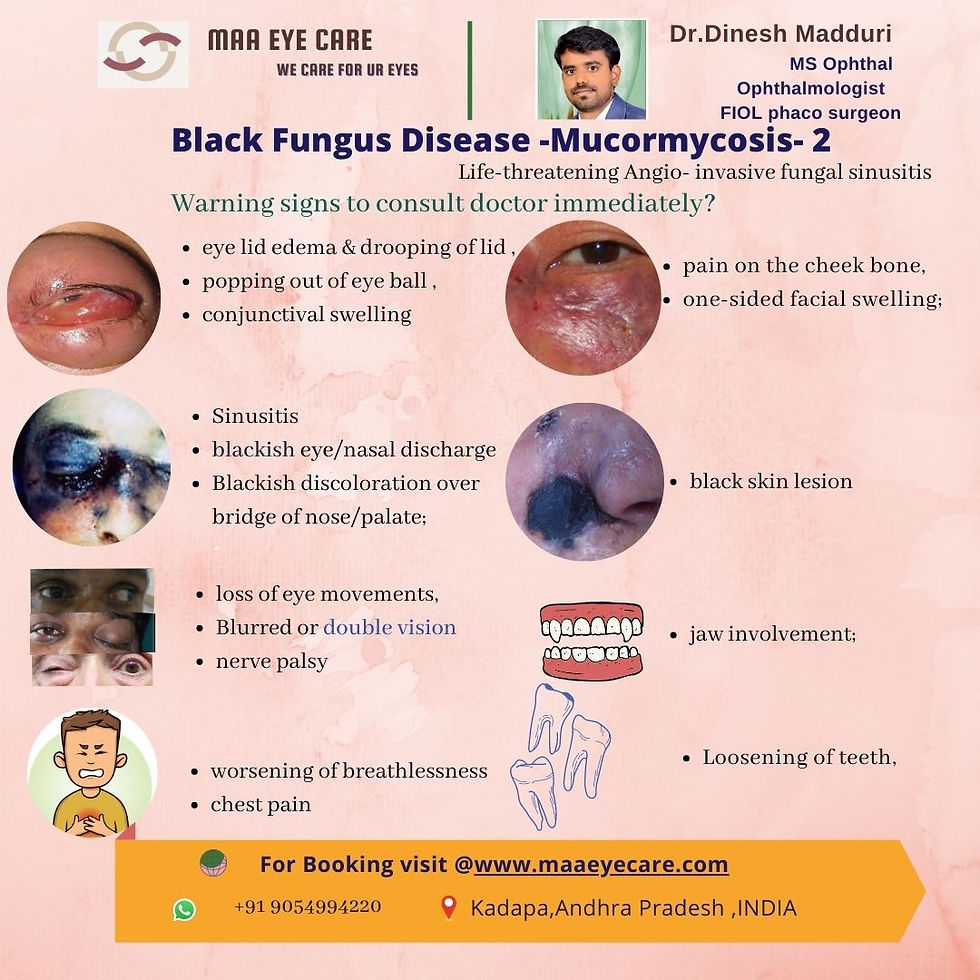
What are the warning signs that needs immediate doctor consultation ?
Nasal stuffiness
Foul smell
Epistaxis - bleeding from nose
Black Nasal discharge- characteristic
Nasal eschar
Eyelid, periocular or facial edema / discoloration
Regional pain – orbit, paranasal sinus or dental pain ,Facial pain
Worsening headache
Proptosis- popping out of eyeball
Sudden loss of vision
loss of Facial sensation
ptosis or drooping of eye lid
double vision
Fever, paralysis, focal seizures
What are the investigations to be done to diagnose it ?
Nasal endoscopy swab for KOH mount
contrast-enhanced MRI or CT Scan of Head.
Clinico-radiological features, coupled with microbiological confirmation
Biopsy of tissue (Histopathological stain )- broad aseptate hyaline hyphae with wide angle branching
Culture on Sabaroud dextrose agar at 25°C - appear as white and black / salt and pepper appearance
Why it is difficult to treat at small set up hospitals ?
Because it needs multi-disciplinary team of doctors comprising radiologist, microbiologist, pathologist, molecular biologist), physician (infectious disease,
neurology, critical care) and surgeon (otorhinolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, neurosurgeon) .
What are the treatments available ?
Guidelines according to The European Confederation of Medical Mycology (ECMM) and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium (MSG ERC) are
Medical :
Intravenous amphotericin B -5-10 mg/kg - 4weeks
followed by
oral posaconazole 300 mg tab
day 1 - 1 tab morning & 1tab evening
day 2 - day 180 - 1 tab daily morning
Hybebaric oxygen therapy if required
Anti fungal treatment is required for 3 - 6 months
Surgical :
If medical treatment fails
Orbital exenteration
aggresive debridement of paranasal sinuses
turbinectomy
palate resection
orbital wall resection

How to prevent this in COVID 19 setting ?
For all patient
strict control of diabetes(FBS <125 mg/dl)
judicious use of steroids and higher antibiotics
For hospitalised patients
Cleaning around mask areas with sponge wet with sanitiser
Changing of oxygen mask weekly
Clean sterile water should be used oxygen therapy
Strict aseptic precautions while administering oxygen
For coma patients
Thorough wash of body atleast weekly with sponge dipped in scrub or sanitiser
For normal or mild covid patient
maintain personal hygeine





Comments